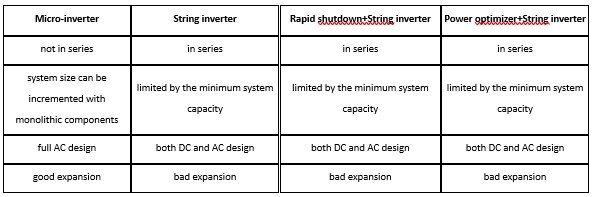
In recent years, traditional inverters are divided into central inverter and string inverter. The traditional PV inverter method is to connect PV panels in series and parallel to form a PV array. Usually, the DC voltage after series and parallel is 600~1500V, then DC is converted into AC and connected to the grid through a central or string inverter. String inverters have many problems, and micro-inverters are emerging inverters that can solve these problems.
However, many people have asked this question: are micro-inverter worth it? Why is this so? Details are given below.
Traditional PV Inverter Method
- String Inverter

A central inverter with inputs for “strings” of panels to be run into a single unit is known as a string inverter. String inverter system solution is suitable for distributed power stations and rooftop PV power generation systems. Usually, a rooftop PV system has only one or two string inverters, depending on the size of solar system.
Pros:
String inverters cost less to install;
Fewer wiring faults as there are fewer string inverters and connections to PV panels;
Easy to troubleshoot, because 1 or 2 string inverters can easily lock the fault location.
Cons:
Easier affected by the environment, such as shading in the series panel;
More difficult expansion;
Shorter life, the warranty is generally 5-12 years;
Panel-level monitoring can’t be achieved, and problems caused by a single panel may not be effectively investigated;
2. Rapid Shutdown + String Inverter

Inverter is the most complex electronic component in a solar system, and it also happens to be the one that fails the most.
Rapid shutdown + String inverter is a commonly used method of PV panels today. In the process of converting DC to AC, DC voltages up to hundreds of volts during operation. Rapid shutdown cuts current to what the human body can handle in microseconds.
In the past two years, many countries have come out regulations indicating that in order to protect the personal safety of firefighters in rescue work, rapid shutdown installation is necessary.
3. Power Optimizer + String Inverter
Power Optimizer + String Inverter is an upgrade on the basis of single string inverter. The power optimizer is a module-level power electronic device with DC input and DC output. Through the series connection with PV modules, the predicted current and voltage technology are used to ensure an optimal working status of modules. According to the buck topology working principle, It is used to solve the influence of PV power plant power generation due to shadow shading, inconsistent orientation or module electrical specification differences, to achieve the MPPT of the modules, and to increase the system power generation.
Emerging PV Inverter Method: Micro-inverter

Micro-inverter is a PV inverter with module-level MPPT function. The full name is micro PV on-grid inverter. Micro-inverter is a device that directly converts the DC generated by each module into AC and then connects to the grid.
Pros:
Independent MPPT control can be performed on each module, which greatly improves the overall efficiency;
Full AC design to avoid the danger caused by DC high voltage;
Good expansion, the system can be freely expanded by monolithic cells;
Panel-level monitoring, which can successfully lock the position even with small problems;
Lifespans up to 25 years
Cons:
Compared with string inverters, the cost per watt of micro-inverter is higher;
Difficult to lock specific inverters for fault detection because of the large number, and also difficult to maintain and replace components;
Not appropriate for stormy places since micro-inverters may double as miniature lightning rods.
Comparison of Micro-inverters with Main Competing Methods
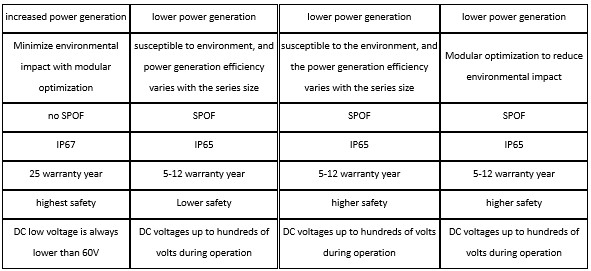
Micro-inverter main disadvantage is the cost per watt is higher. However, in distributed PV systems such as residential scenarios, after considering the higher total system efficiency, calculating LCOE (kWh cost) or IRR (return on investment ratio) , it has more advantages than string inverter. And in recent years, the cost of micro-inverter has decreased significantly.
Overall, micro-inverters, while a „rookie” among inverters today, are really worth it.
Introduction of BENY Micro-inverter and Supporting Equipment
- Single-in/Quad-in Micro-inverter(1-in-1/2-in-1/4-in-1/8-in-1)
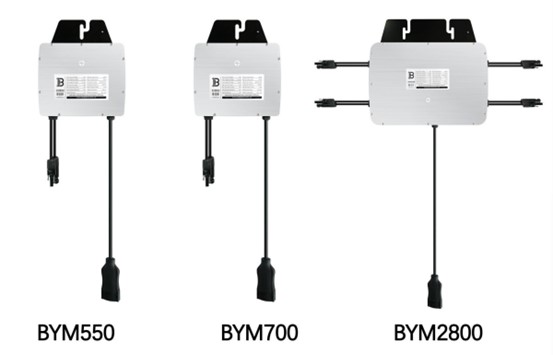
With the maximum output power of 721 VA, BENY BYM550/BYM700 micro-inverter connect to 1 panel and the maximum output power of 2940 VA, BENY BYM2800 micro-inverter connect to 4 panels, enable module-level maintenance and management of the PV station by monitoring power generation of each module.
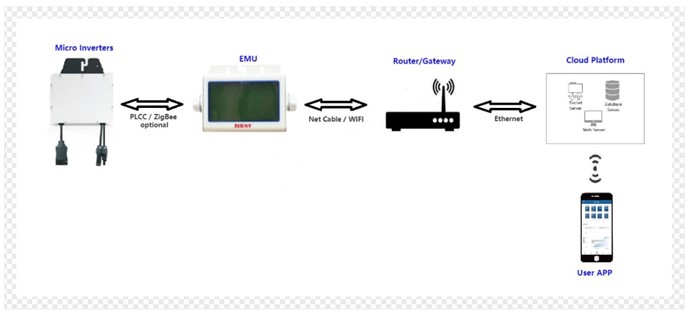
2. Monitoring Device EMU
EMU is a gateway that acts as a monitoring device. When using a model BYR990, it needs to be equipped with an LC filter.
One EMU can connect up to 8 micro-inverters. Its main functions are: improve the PLC communication effect in the LAN where monitoring device and micro-inverter are located, and prevent the interference of grid noise; filter out the interference of PLC communication signal to grid; avoid crosstalk between multiple sets of EMUs and micro-inverter systems, which will affect the communication effect.
3. Parallel Optimizer BYPO
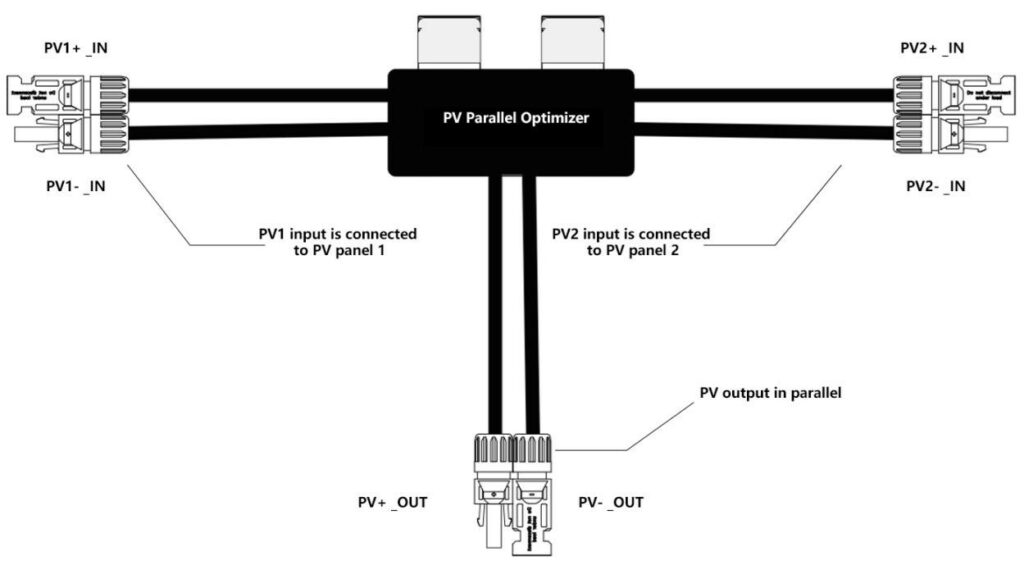
BYPO-2 is a PV parallel optimizer. Users can use BYPO-2 to connect PV modules in parallel to increase the output current of the PV array, thereby obtaining greater output power. It has the features of ultra-low voltage drop and ultra-low loss, which can solve the problem that the current backflow reduces the life of PV modules or damages PV modules in parallel. and can improve the MPPT efficiency of PV modules in parallel use. PV parallel optimizer also has a module shutdown function.
Both the PV parallel optimizer and power optimizer include optimizations, but they are used for very different purposes.
4. Data Analysis System BYDAS
BYDAS is an online monitoring panel and micro-inverter status. In order to give users a better experience, this system is still being updated and optimized.
BENY Micro-inverter Advantages
- the third generation semiconductor technology GaN HEMT is used to replace Si MOSFET for the main topology of the flyback conversion, and its own patented power control optimization algorithm is used to greatly improve the conversion efficiency of microinverter and reduce system loss.
- The products are fully designed, with real materials, the main control chips, power devices, magnetic components and resistance components are all selected from the top international manufacturers, MTBF> 25 years. The structure and heat dissipation design are fully designed to ensure that it can still work at full load when the ambient temperature is 55℃.
- Original, own patented parallel optimizer,using BYM series microinverter to support the super input current, realize 1-in-1->2-in-1, 4-in-1->8-in-1.
- About the communication method, our gateway and micro-inverter use PLCC/Zigbee. According to different application environments, corresponding solutions can be configured to ensure communication quality. The communication between the gateway and the Ethernet router can be connected by RJ45 cable. It’s a mature and reliable solution, the communication quality is guaranteed, and the user and the installer do not need any network distribution action, which is friendly to operate and low difficulty.
Conclusion
Currently, micro-inverter is a friendly choice for achieving the highest power generation efficiency in PV systems, especially residential rooftop, where panels are small and easily shading from surrounding objects. And micro-inverter is also better than traditional inverter in terms of safety: the full AC design reduces potential risks caused by DC high voltage; panel-level monitoring effectively avoids risks. The 25-year lifespan is also more reliable than string inverter.
If PV system owner chooses micro-inverter after evaluating their own conditions and inverter usage, contact us right now for free electrical consultation and quotation.
Website Link: https://www.beny.com/new/solar-inverter-guide-are-microinverters-worth-it/